When you’re dealing with vehicle data, whether for a fleet, an insurance claim, or just curiosity about your own car, the integrity of a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is paramount. Validating & Decoding Generated VINs isn't just about punching numbers into a system; it's about ensuring data accuracy, preventing errors, and unlocking a trove of crucial vehicle information. Think of it as the ultimate diagnostic for a car's identity, a process that separates reliable data from potential digital junk.
No one wants to make critical decisions based on faulty information. A generated VIN, whether from a software tool or an external database, needs to stand up to scrutiny. Understanding how to validate it and then decode its secrets empowers you to trust the data and make informed choices, from ordering the right part to assessing a vehicle's history.
At a Glance: Key Takeaways
- VINs are unique vehicle fingerprints: Since 1981, they're 17 characters packed with specific, coded information.
- Validation is critical for accuracy: It confirms a VIN is structurally sound and likely legitimate, preventing errors and fraud.
- Decoding unlocks vehicle data: Each character or group of characters reveals details like country of origin, manufacturer, model, engine, model year, and plant.
- The NHTSA VIN Decoder is a gold standard: It offers robust offline and online capabilities, comprehensive databases, and manufacturer-specific logic.
- Offline decoding is fast and efficient: Ideal for basic identification where speed and minimal resources are key.
- Online decoding provides full detail: Accesses safety ratings, recalls, and granular specifications via API integration.
- Applications are wide-ranging: From vehicle history reports to fleet management and parts matching.
The Unseen Language of Vehicles: What is a VIN, Really?
Before we dive into validation and decoding, let’s quickly establish our foundation. A Vehicle Identification Number, or VIN, is essentially a 17-character serial number. But it's far more than just a random string. Standardized globally since 1981, this alphanumeric code is the vehicle's unique identifier, a compact autobiography etched into its chassis.
You can spot a VIN in a few common places: usually at the base of the windshield on the driver’s side, on a sticker in the driver’s side door jamb, or often found on official documents like vehicle titles and registration. Each of its 17 characters, a mix of letters and numbers, carries a specific meaning, collectively describing everything from where it was made to what kind of engine it has.
Why Validation Isn't Just Good Practice—It's Essential
Imagine a scenario where you're trying to purchase a used car online, or perhaps you're an insurer processing a claim. The first piece of data you encounter is the VIN. If that VIN is faulty—typo-ridden, maliciously altered, or simply a randomly generated VIN number without adherence to standards—the consequences can range from minor inconvenience to significant financial loss. This is why validating a VIN is non-negotiable.
The Stakes of an Invalid VIN
- Data Accuracy: An invalid VIN can lead to incorrect vehicle identification, which can cascade into wrong parts orders, inaccurate insurance quotes, or even misidentification in legal contexts.
- Fraud Prevention: Scammers often use altered or completely fabricated VINs to obscure a vehicle's true identity, hide salvage titles, or misrepresent a car's history. Validation helps flag these red flags early.
- Safety & Compliance: For recall management or safety checks, having the correct VIN is crucial. An invalid VIN means a vehicle could miss critical safety notices.
- Operational Efficiency: In large operations like fleet management or auto dealerships, a robust validation process saves immense time and resources by preventing errors down the line. Entering bad data at the start is a costly mistake.
Deconstructing the VIN: How to Validate Its Integrity
Validating a VIN isn't just about checking if it's 17 characters long. It involves a specific algorithmic check and an understanding of its structural components. The international standard for VINs is ISO 3779, which dictates the layout and content.
The Check Digit: The VIN's Built-In Validator
The most critical component for immediate validation is the ninth character of the VIN. This is the check digit, a single character (0-9 or X) that is mathematically derived from all the other 16 characters in the VIN.
Here's a simplified explanation:
- Each character in the VIN is assigned a specific numerical value.
- Each of these values is multiplied by a weighted factor based on its position.
- All these products are summed up.
- The sum is divided by 11.
- The remainder must match the check digit. If the remainder is 10, the check digit is "X."
If the calculated check digit doesn't match the one in the VIN, the VIN is invalid. This system is incredibly powerful because it can detect transcription errors (like a single typo) with a very high degree of accuracy. It's the first line of defense against a faulty VIN.
Structural Compliance: Beyond the Check Digit
Beyond the check digit, a VIN must also adhere to specific structural rules:
- 17 Characters: Not 16, not 18. Exactly 17.
- Valid Characters: Only uppercase letters A-Z (excluding I, O, Q to avoid confusion with 1, 0, and 9) and numbers 0-9 are permitted.
- Manufacturer-Specific Logic: While the overall structure is standardized, specific character positions might have different meanings depending on the manufacturer, which brings us to decoding.
Decoding the Secrets: Unpacking the VIN's Story
Once you've validated that a VIN is structurally sound and passes its check digit, the real fun begins: decoding it. This process extracts all the embedded information, transforming a seemingly random string into a detailed vehicle specification.
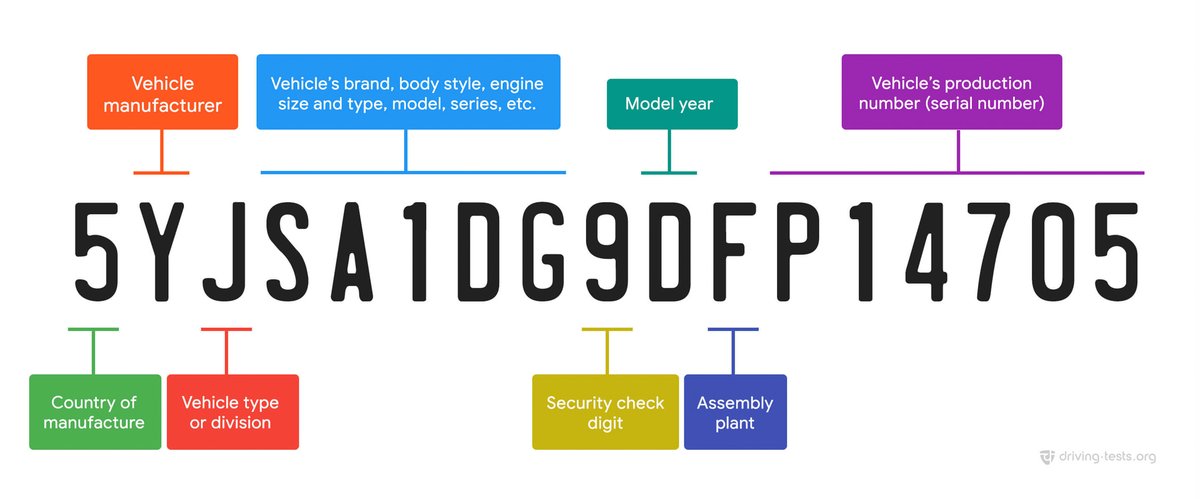
A standard VIN breaks down into three main sections:
1. World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) - Characters 1-3
- Character 1: Geographic Region/Country. Identifies the country of assembly. For example, '1' or '4' or '5' for the United States, '2' for Canada, '3' for Mexico, 'J' for Japan, 'W' for Germany, 'Z' for Italy, etc.
- Character 2: Manufacturer. Identifies the manufacturer within that region (e.g., 'G' for General Motors, 'F' for Ford, 'T' for Toyota).
- Character 3: Vehicle Type/Division. Can specify the type of vehicle (e.g., passenger car, truck, bus) or a specific manufacturing division.
Example: A VIN starting with "1G" likely indicates a General Motors vehicle made in the United States.
2. Vehicle Descriptor Section (VDS) - Characters 4-9
This section describes the general characteristics of the vehicle. These characters' meanings can vary significantly between manufacturers, but typically include:
- Characters 4-8: Body Type, Engine Type, Model, Series, Restraint System. These positions are manufacturer-specific but typically detail aspects like sedan, coupe, pickup truck, engine size/type (V6, V8, electric), specific model line, and safety features.
- Character 9: Check Digit. (As discussed above, this validates the entire VIN's integrity.)
3. Vehicle Indicator Section (VIS) - Characters 10-17
This is the specific identifier for the vehicle itself, often called the production or serial number.
- Character 10: Model Year. This is a critical one. It uses a specific code (e.g., 'A' for 1980, 'B' for 1981, 'Y' for 2000, '1' for 2001, '9' for 2009, 'A' for 2010, etc.). It cycles through letters and numbers. Sometimes, for older VINs or specific manufacturers, position 7 might also be relevant for model year accuracy.
- Character 11: Plant of Manufacture. Identifies the specific factory where the vehicle was assembled.
- Characters 12-17: Production Sequence Number. These are the last six digits and represent the unique serial number of that specific vehicle as it came off the assembly line.
Quick Tip: Many online tools struggle with accurately identifying model years across different decades, especially as the alphanumeric sequence repeats every 30 years. A robust decoder needs to account for this cycle and potentially use other VIN positions or manufacturer data to confirm the correct decade.
The Gold Standard: NHTSA's vPIC Decoder
When it comes to comprehensive and trustworthy VIN decoding, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) offers a world-class solution: its vPIC Decoder. This isn't just another online tool; it's a multi-platform, highly reliable system that sets the industry benchmark for VIN information.
A Dual-Mode Powerhouse: Offline vs. Online
The NHTSA vPIC Decoder offers a unique advantage with its dual functionality, catering to different use cases:
Offline Capabilities: Speed and Efficiency
For tasks demanding instant responses and minimal resource usage, the offline mode is a game-changer.
- Speed Demon: Boasting <1ms response times, it's 500x faster than typical online queries. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time data processing, like OBD-II diagnostic apps.
- Resource-Light: The offline WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier) database is incredibly efficient, using only ~100KB of memory. This makes it perfect for embedded systems, mobile applications, or scenarios with limited connectivity.
- Core Identification: In offline mode, you can quickly get fundamental details:
- VIN Validation: Confirms ISO 3779 compliance and check digit accuracy.
- Manufacturer Identification: Pinpoints the maker using its extensive 2,015+ WMI codes (far exceeding industry standards).
- Accurate Model Year Extraction: Reliably identifies model years from 1980 to 2039, addressing the alphanumeric cycle challenge.
- Region of Assembly: Determines the country or region of manufacture.
- Manufacturer-Specific Decoders: Even offline, it incorporates logic for major brands like Mercedes-Benz, Ford, GM, and Toyota/Lexus, allowing for more precise decoding where general standards might be ambiguous.
When to use offline: Speed-critical applications, basic vehicle identification, initial data filtering, mobile apps needing immediate feedback.
Online Capabilities: The Full Data Spectrum
For the most detailed and current information, the online mode, integrating with the official NHTSA vPIC API, is indispensable.
- Comprehensive Vehicle Specifications: Unlocks an exhaustive list of attributes, including detailed engine type, transmission specifications, fuel type, body style variations, and more.
- Safety & Compliance Data: Crucially, it provides access to:
- Safety Ratings: Information from crash tests and safety assessments.
- Recalls: Any active or past recalls associated with the VIN.
- NCAP Data: New Car Assessment Program results.
- Global Coverage: While strong for North America, it also offers comprehensive coverage for Europe and extensive data for Asia, including special vehicle types like motorcycles and electric cars.
- No API Key, Free Access: A major advantage, making it accessible for developers and businesses without subscription barriers.
- Caching: Built-in caching further optimizes performance for frequently requested VINs.
When to use online: Detailed vehicle history reports, insurance assessments, in-depth parts lookup, pre-purchase inspections, fleet management needing full spec details.
Why vPIC Stands Out
The NHTSA vPIC Decoder isn't just a tool; it's a robust ecosystem for VIN intelligence. Its blend of speed, accuracy, comprehensive data, and ease of access makes it an unparalleled resource for anyone working with vehicle data. Its extensibility for custom manufacturer decoders also means it can grow and adapt to evolving automotive landscapes.
Real-World Applications: Where VIN Validation & Decoding Shines
The ability to validate and decode VINs isn't just a technical exercise; it's a foundational capability that underpins numerous industries and personal decisions.
1. Automotive Sales & Dealerships
Ensuring VIN accuracy at every stage—from inventory management to sales and titling—is paramount. Decoding helps sales staff quickly pull up exact vehicle specifications, features, and even specific trim levels, leading to faster, more accurate sales.
2. Fleet Management
For businesses managing a fleet of vehicles, accurate VIN data is critical. Decoding helps track maintenance schedules, ensure compliance with emissions standards, manage tire and part inventories specific to vehicle models, and monitor recall statuses across the entire fleet. It helps to streamline operations and reduce downtime, making fleet management more efficient.
3. Insurance & Accident Reconstruction
In the insurance industry, the VIN is the bedrock of every policy and claim. Decoding helps verify the exact vehicle involved, its features, and specifications for accurate valuation and claim processing. In accident reconstruction, a precise VIN allows for access to vehicle-specific crush data and structural information, aiding in investigations.
4. Parts & Service Departments
Have you ever tried to order a part for your car and found there are five different options for the "same model"? The VIN eliminates this guesswork. Decoding provides the precise engine, transmission, and trim level, ensuring the correct part is ordered the first time, reducing returns and improving service efficiency. This is particularly vital for avoiding costly errors.
5. Vehicle History Reports
Any reputable vehicle history report service (like CarFax or AutoCheck) starts with a validated VIN. The decoded information forms the basis for cross-referencing accident history, odometer discrepancies, previous owners, and salvage titles, providing critical transparency for buyers.
6. Classic Car Restoration & Identification
For classic car enthusiasts, decoding a VIN can be like uncovering an archaeological find. It confirms authenticity, original specifications, and can even identify rare models or specific production runs, adding immense value and historical accuracy to restoration projects. This ensures you're working with genuine data, not just anecdotes.
7. OBD-II Apps & Diagnostics
Many modern diagnostic apps for cars utilize the VIN to pull up manufacturer-specific trouble codes and diagnostic information. Fast, offline VIN decoding is particularly valuable here, allowing apps to quickly identify the vehicle and present relevant diagnostic options without needing an internet connection.
Common Misconceptions & Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with powerful tools like the NHTSA vPIC Decoder, it's wise to be aware of potential pitfalls.
- Pre-1981 VINs: Vehicles manufactured before 1981 used varying VIN formats, often shorter and non-standardized. Modern decoders are typically designed for 17-character VINs and won't accurately decode older formats. Manual research is often required for these.
- Manufacturer Variations: While the overall structure is standard, some manufacturers interpret certain VDS positions differently. A good decoder (like NHTSA's) will account for these nuances, but generic tools might miss them.
- Physical VIN Tampering: No software can validate a physically altered VIN on a vehicle itself. Always compare the VIN in multiple locations (dashboard, door jamb, title) to ensure consistency. If they don't match, walk away.
- "Generic" VIN Generators: Be wary of simple online tools that claim to generate your VIN number randomly. While they might produce a 17-character string, it’s unlikely to pass the check digit algorithm or correspond to any real vehicle. These are for illustrative purposes at best, not for actual data.
- Over-reliance on Single Source: Always cross-reference VIN data when critical decisions are at stake. While NHTSA is world-class, combining its data with vehicle history reports or direct manufacturer information provides the most robust picture.
Mastering Vehicle Identity for Data Integrity
In an increasingly data-driven world, the VIN stands as a critical identifier. For anyone involved with vehicles—from individual car owners to massive automotive enterprises—the ability to confidently validate and decode VINs is no longer a niche skill, but a fundamental requirement for data accuracy and operational excellence.
By understanding the VIN's structure, leveraging robust tools like the NHTSA vPIC Decoder, and being aware of common pitfalls, you can unlock a vehicle's complete story. This expertise ensures that every decision you make, every part you order, and every transaction you conduct is built on a foundation of trusted, accurate information.